Cenozoic Era
65 Million Years Ago to Present
The Cenozoic was a time of change.
Flowering plants were common.
The big reptile rulers were gone and life started to develop in other directions. The mammals which had remained small in the time of the dinosaurs started to develop and diversify.
But the big ruler of the early Cenozoic was the bird. Certain bird species developed into 6-foot tall terror birds with large carnivorous beaks. The Gastornis was one of these.
Horses began to evolve about 54 million years ago (see the heading Horse Evolution above).
The earliest ancestor of the whale, Ambulocetus ("walking whale") lived about 50 million years ago. This was a land dwelling animal about 10 feet long, 660 pounds, and heard through his jawbone. Ambulocetus is thought to be the "missing link" between Andrewsarchus and the fully aquatic whale.
This was also a time when primates developed. "The Link", initially referred to as Ida and now with the scientific name Darwinius masillae, is thought to be our earliest known ancestor. This 47 million year old fossil appears to be the stage of primate development just before lemurs and primates split. This would make it the earliest discovered link in the human lineage.
About 40 million years ago grass developed. This is about the same time that India, which had broken away from Antarctica, smashed into Asia and started the creation of the Himalayan mountains.
Also, about 40 million years ago, mammals learn to fly. Below is a cast of a 40 million year old bat. Not much difference between then and now.
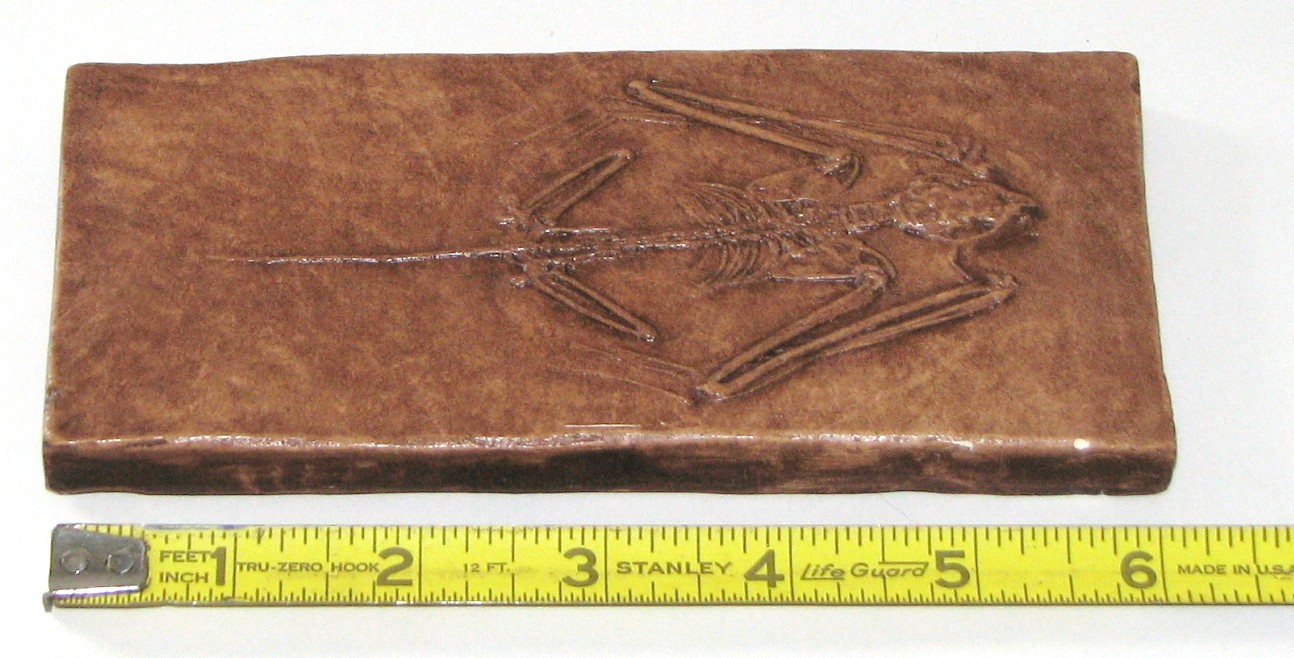

These are rhinoceros fossils about 38 million years old.
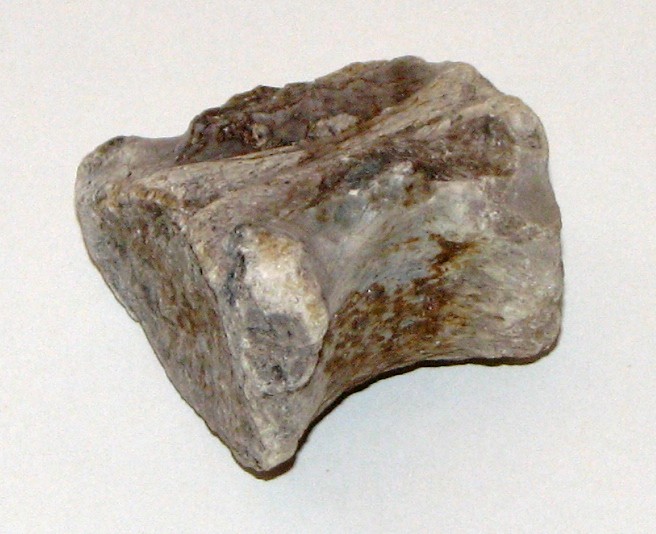


Above, on the left, is a rhinoceros vertebra. On the right is a jaw section with a tooth. These are both from North America where the rhinoceros appears to have originated. The rhinoceros of 38 million years ago was noticeably different than the rhinoceros of today.
36 million years ago Antarctica began to freeze. This started global cooling which seems to have caused about 20% of life to die out.
Indricotherium lived 30 - 25 million years ago and was the largest land mammal ever. At 15 feet high and weighing in around 15 tons, Indricotherium is thought to be the largest size possible for a mammal without causing overheating.
Indricotherium was recently re-named Paraceratherium.
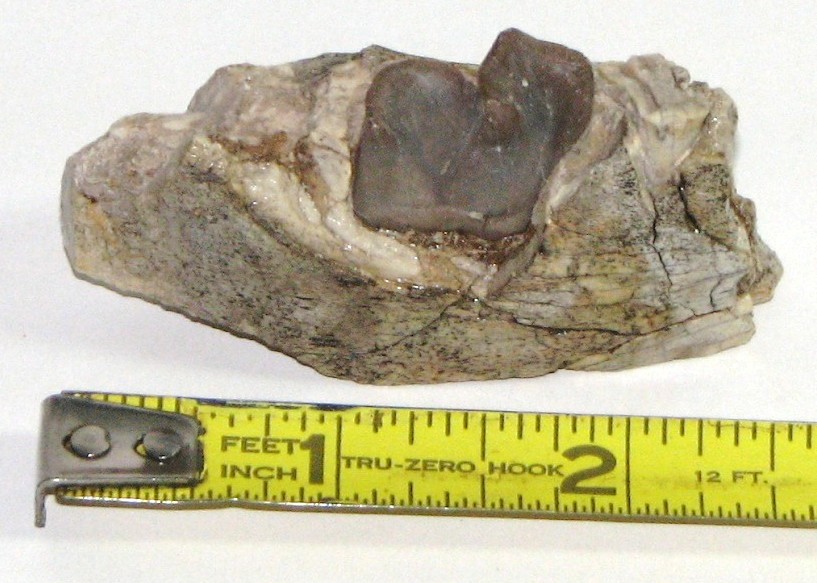
The toe bone below is from a North American camel - 26 million years old. This toe bone is 3/8 inches long.

North America also had lions, and giraffes. They looked different from what we now know but they originated here.
The tooth below (on the right) is from Carcharodon megalodon. We only know Megalodon from its teeth. Like modern sharks it was composed mostly of cartilage which does not survive as a fossil. The tooth on the left is from a modern Great White shark.
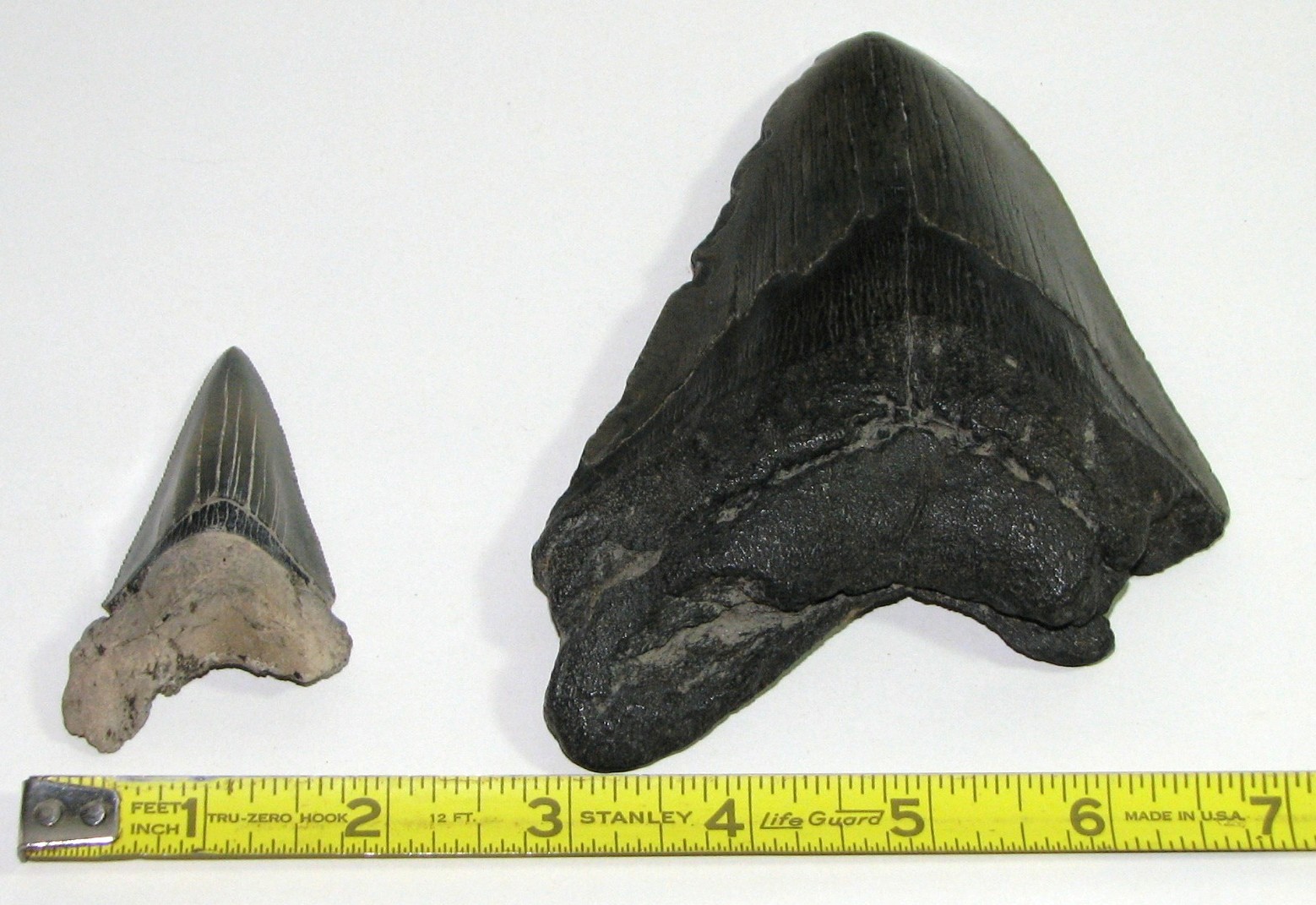

The Great White shark is about 25 feet long. The megalodon is thought to have been up to about 53 feet long and been able to open its mouth to 6.5 feet wide. Megalodon teeth can measure over 6 inches along a side.
The Megalodon lived from about 16 to 1.6 million years ago. Its diet included dolphins and whales.
The Mastodon may go back to 40 million years ago, the Mammoth goes back to around 4.8 million years ago.
These are 2 different animals.
The tooth below, on the left, is from a Mastodon. The tooth on the right is from a Mammoth.
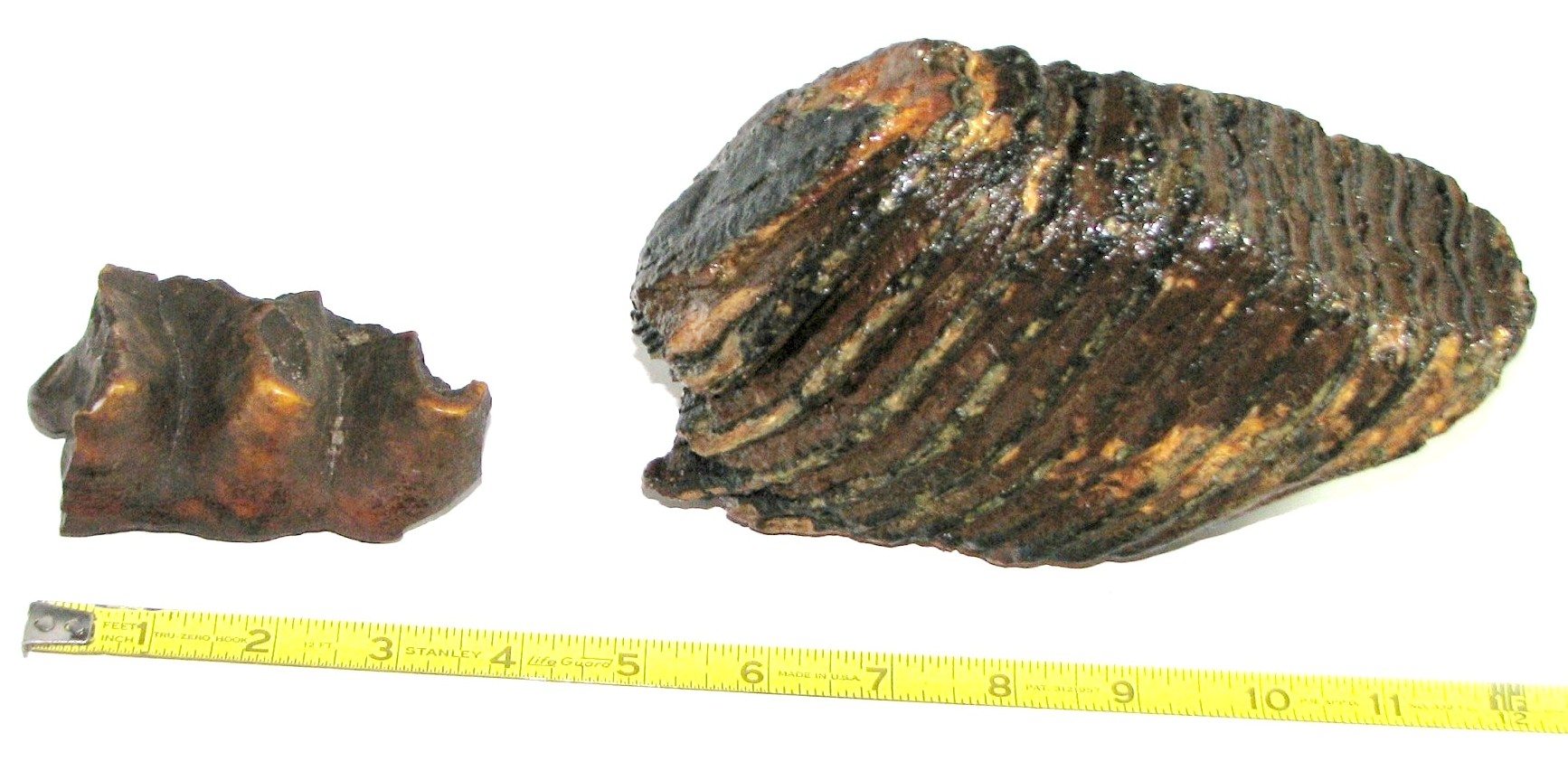

The Mastodon tooth has deep ridges - this was an animal that ate tough plants.
The Mammoth tooth is smoother on top, similar to the modern day elephant. Mammoth ate softer plant material.
Below is a reproduction of a juvenile Mammoth jaw section showing how the Mammoth teeth sat in the jaw.
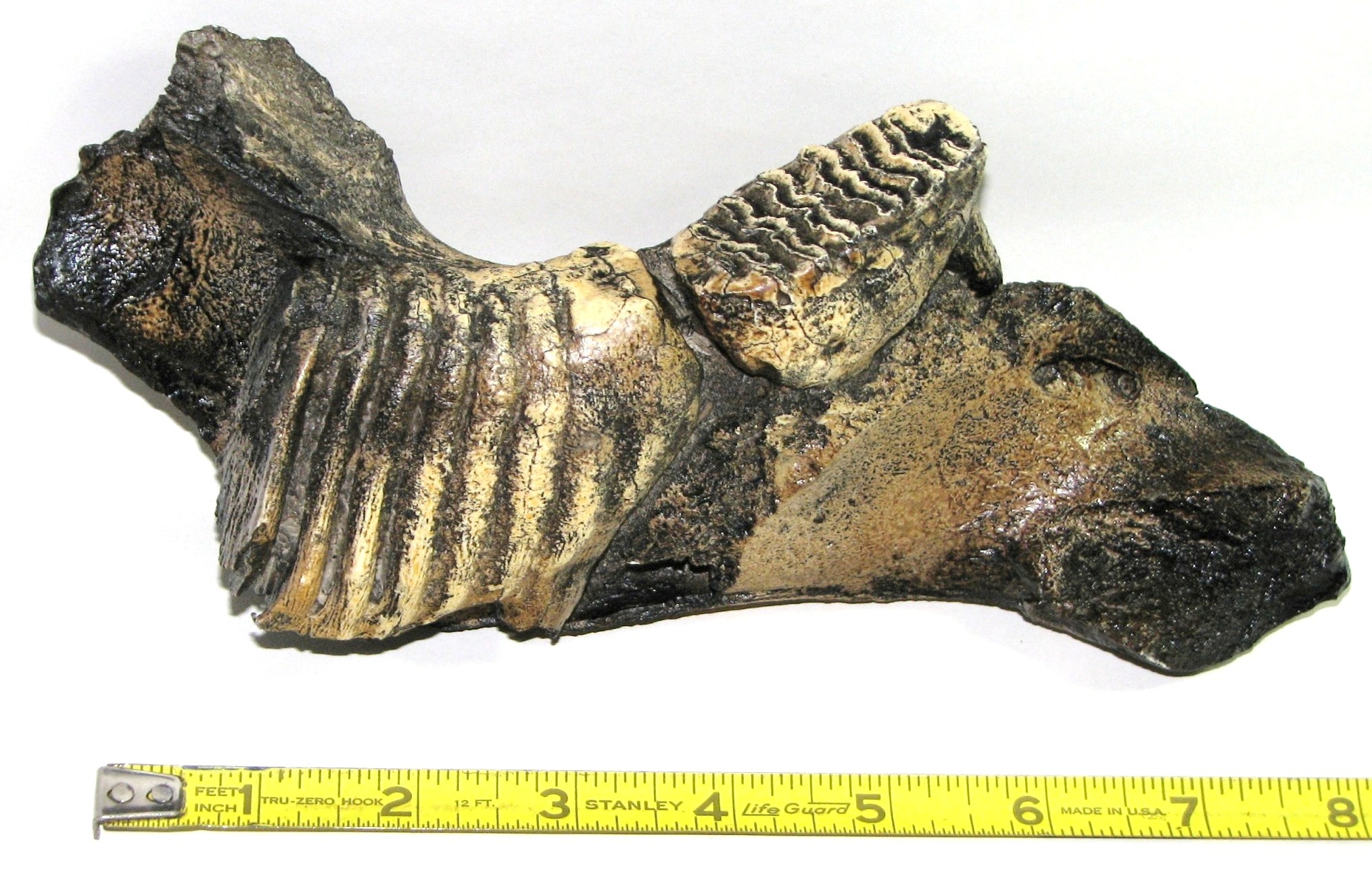

Much is known about the Mammoth since many intact Mammoths have been found. One was found 638 pounds of grass in its stomach.
Mammoth hair on the Wooly Mammoth could be up to 3 feet long. The outer coat was a thick straw-like hair while the undercoat was a finer fluffier hair.
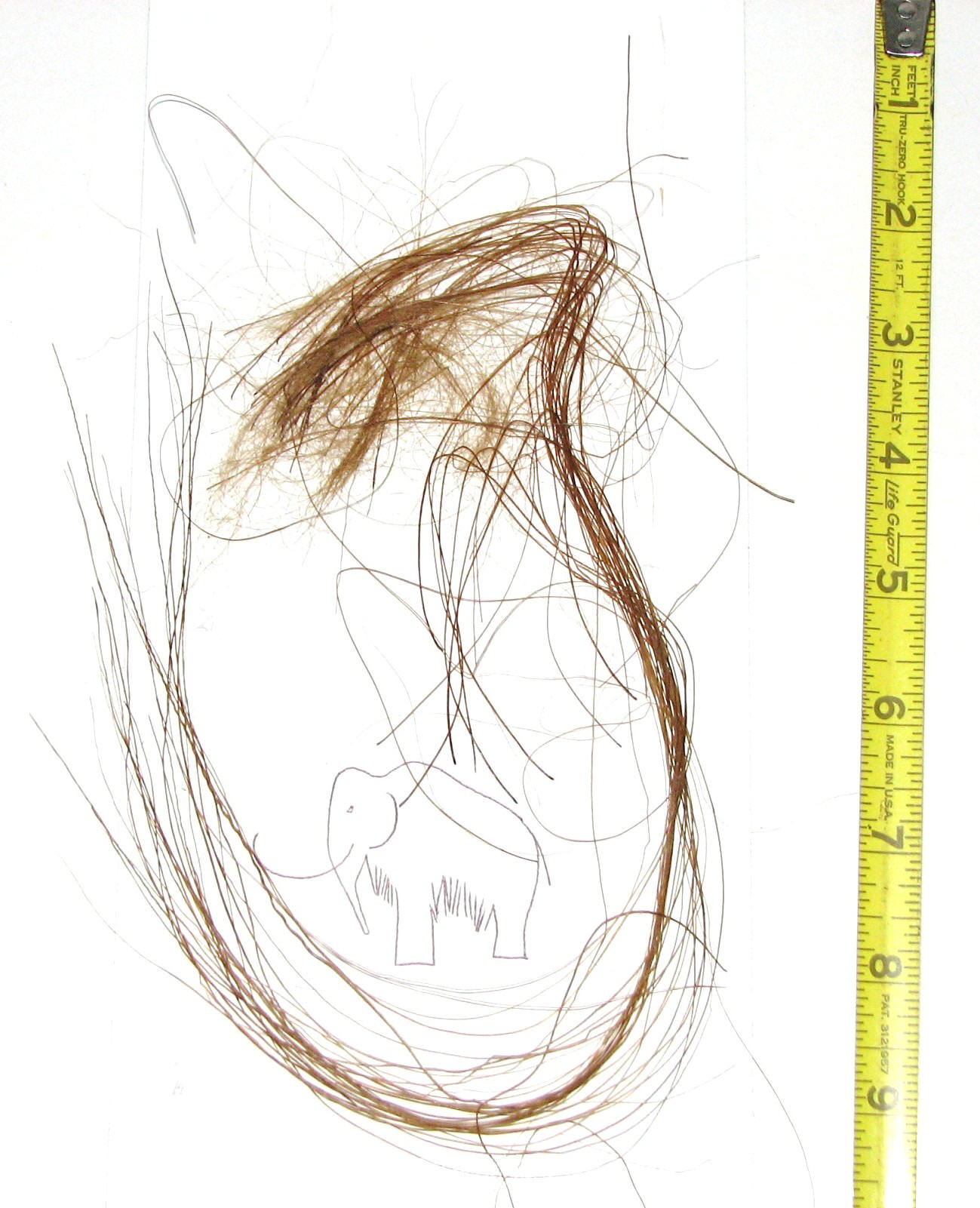


The hair on the left is the outer coat, the hair on the right is the undercoat.
There were actually about 8 Mammoth species. Some were not wooly.
Male Mammoths stood approximately 11.5 feet tall, females stood approximately 10 feet tall. The tusks on the Imperial Mammoth of North America could grow to 14 feet long.
The Mammoth and the Mastodon became extinct about 5000 years ago. There could be several reasons: weather changes, vegetation changes, hunted to extinction by modern man. The actual reason or reasons are unknown.
Around 1.9 million years ago there was a giant sloth - Megatherium. Megatherium grew to 19.5 feet long and probably weighed 4 tons. Megatherium went extinct about 8000 years ago.
The Cave Bear lived between 1.9 million years ago and 28,000 years ago. He was related to the modern Brown Bear and was the size of today's largest bears. The "cave" name of the Cave Bear came from what seems their tendency to actually live in caves. Bear usually use caves only for hibernating.
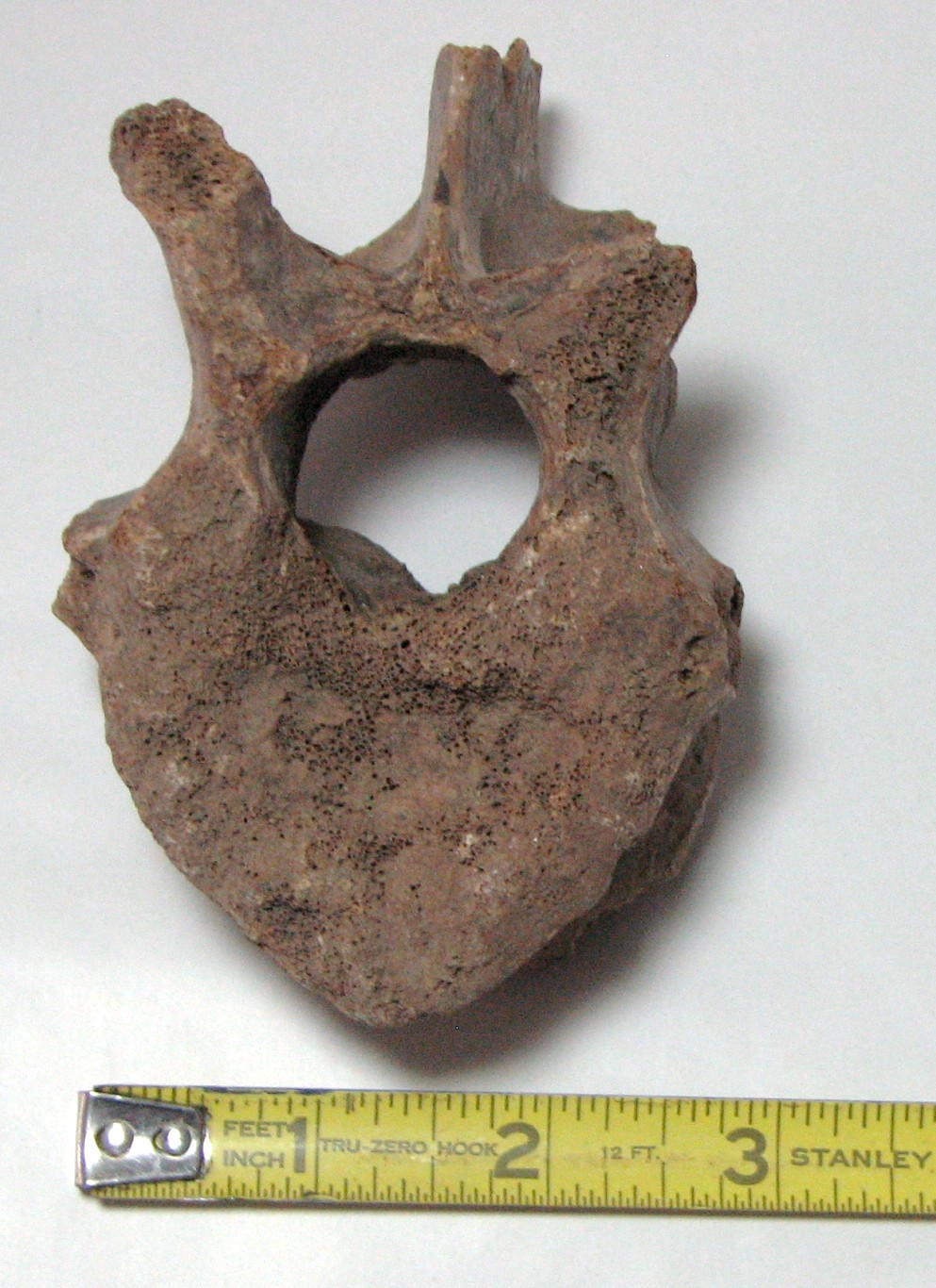


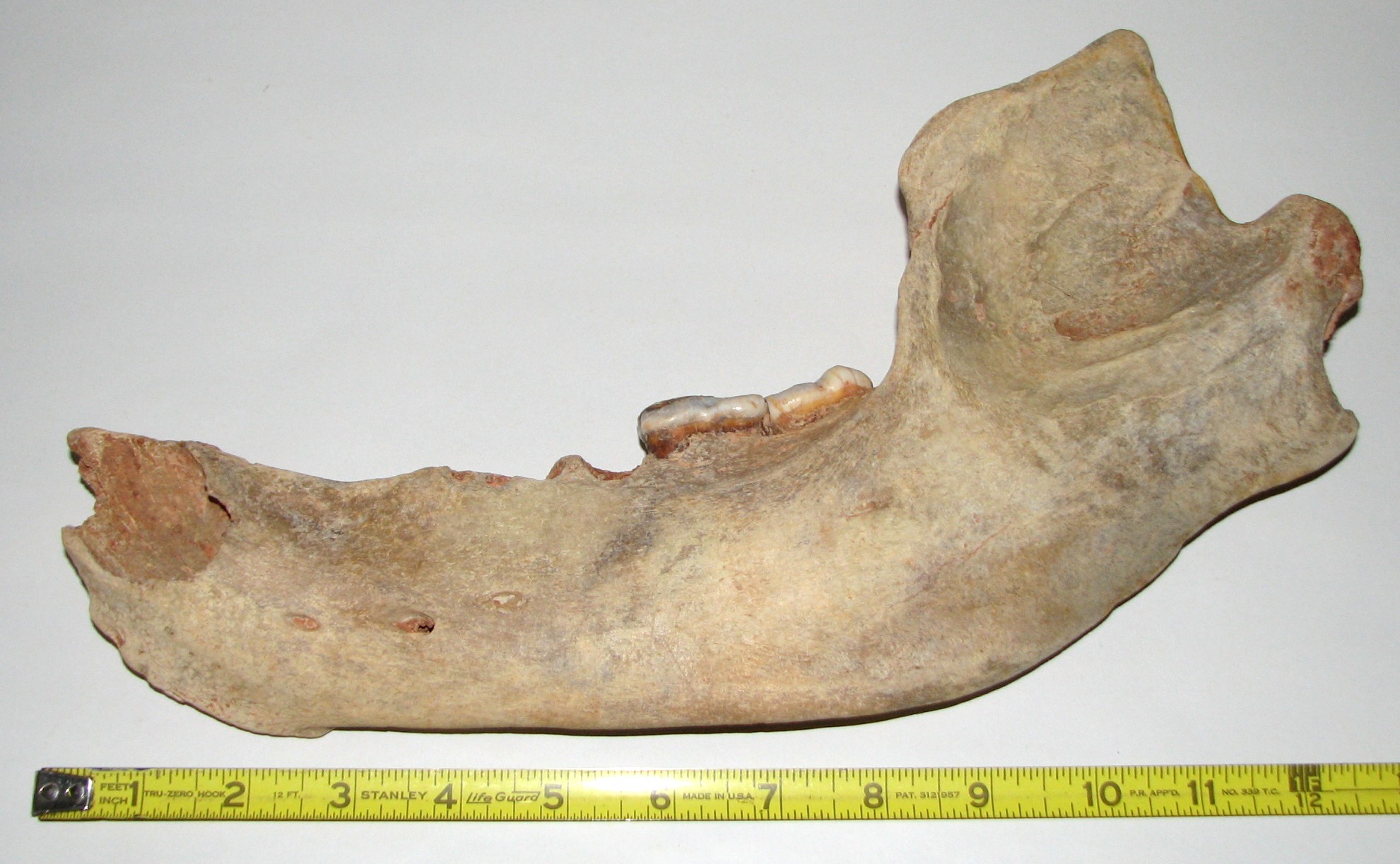
Above, top right is a Cave Bear vertebra.
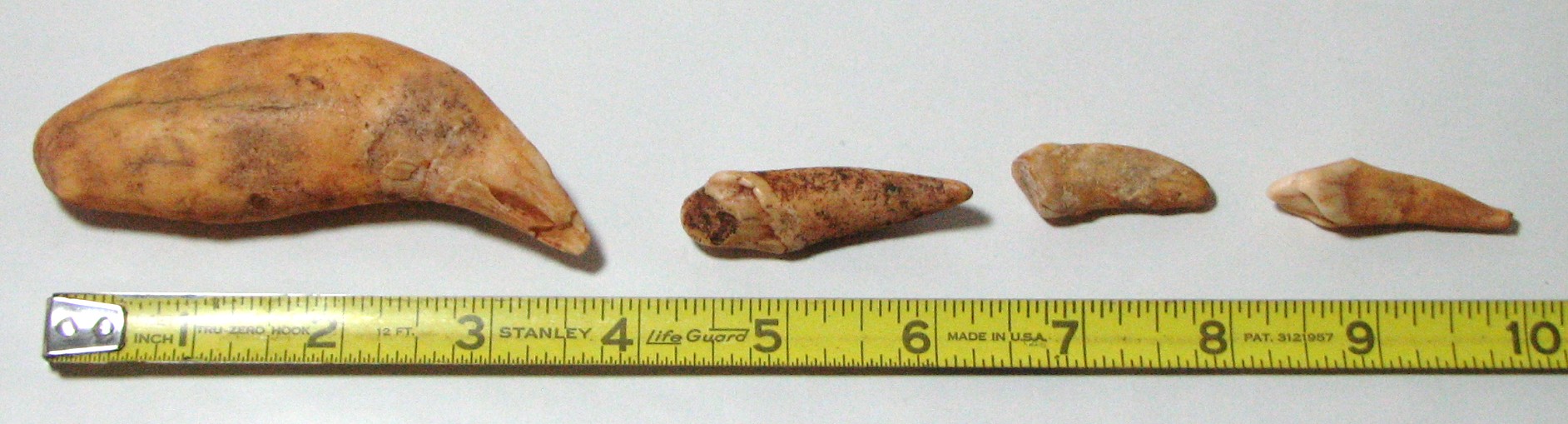
Top left are Cave Bear teeth and, bottom, is the right section of a Cave Bear jaw that the teeth would fit in. The first tooth on the left in the top photo is the canine with the root.
The Cave Bear is thought to have been a herbivore ... mostly. Some Cave Bear teeth indicate that they may have chewed on bones at times. They may have been omnivores much like today's bears.
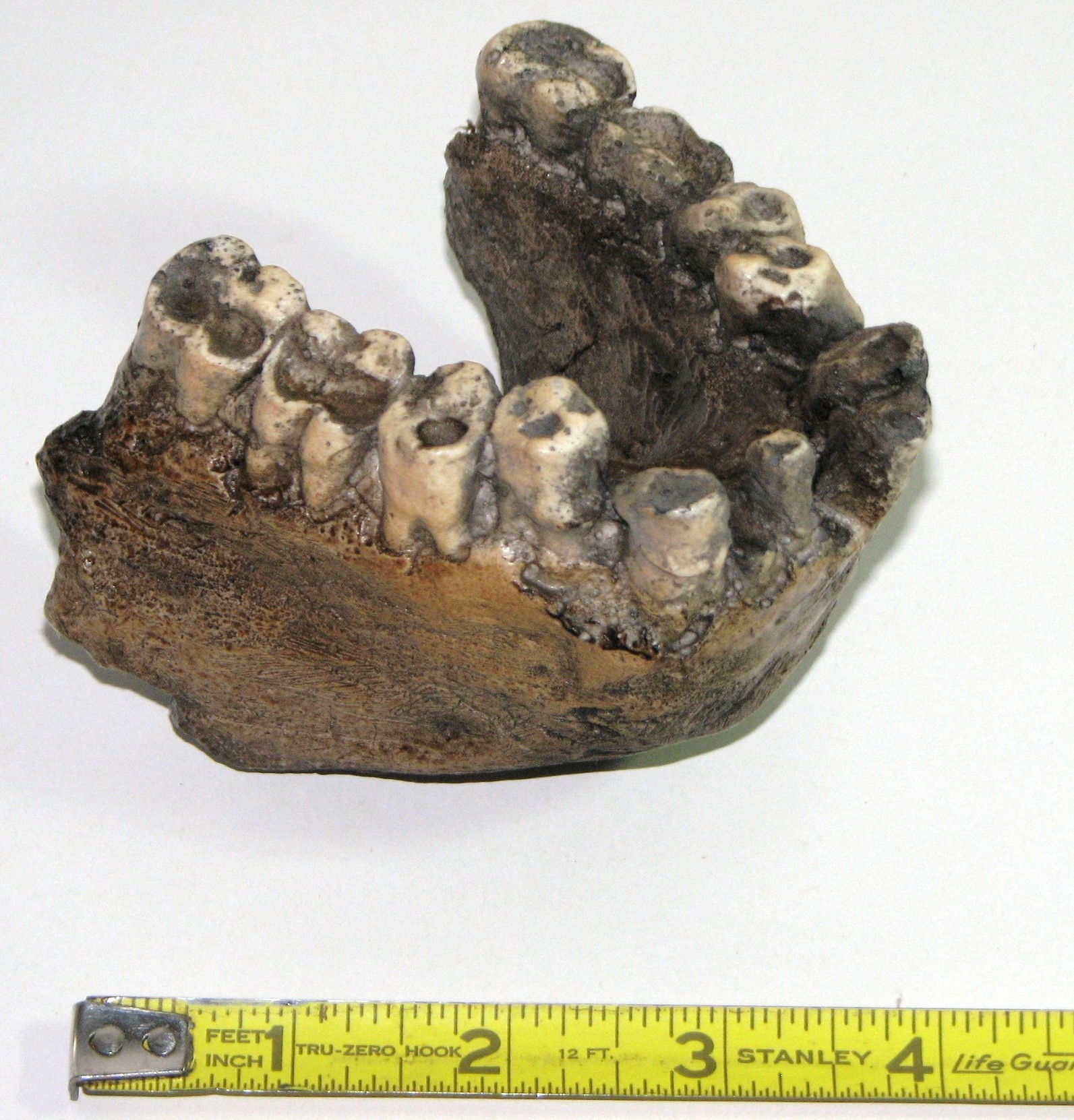
A relatively unknown animal of the Cenozoic is Gigantopithecus.
Gigantopithecus was the largest known ape and became extinct about 100,000 years ago.
Gigantopithecus stood about 10 feet tall and, judging from the teeth and food supply in the area (China), probably had a diet of bamboo.
The size of Gigantopithecus is based on known jaw sections (reproduction below). Very little has been found from this animal.
Exhibits will be updated as more become available. Keep checking back!